In this post I want to detail my experience monitoring Tomcat with SCOM 2012. In my case the application servers were Windows Server 2008 R2 running Tomcat 7 as a windows service. When Tomcat is running as a windows service SCOM does not automatically detect the Tomcat instance. So this blog post will focus around monitoring Tomcat Running as windows service and the steps you have to take to get this working.
There are two other things you need to take care of that I do not cover in this post. These are:
#1 The application servers that are hosting your Tomcat need to have the Agent Proxy enabled.
See this link on how to do this:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh264858.aspx
or this link to enable proxy for all agents:
http://www.bictt.com/blogs/bictt.php/2012/08/24/scom-2012-enable-agent-proxy
#2 You will need to deploy BeanSpy to your Tomcat server first.
See step 5 of this post on how to do this:
BeanSpy is a WAR file. WAR files are used to deploy web applications to Tomcat.
BeanSpy is essentially a web application deployed to Tomcat that SCOM uses to gather data.
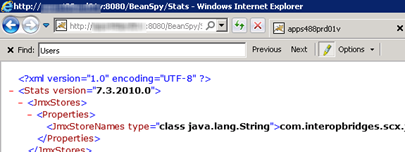
After you deploy BeanSpy verify that it is working. Access this URL:
http://TOMCATSERVERNAME:8080/BeanSpy/Stats
If an XML page such as the one in the following screenshot appears then we have verified BeanSpy is working.
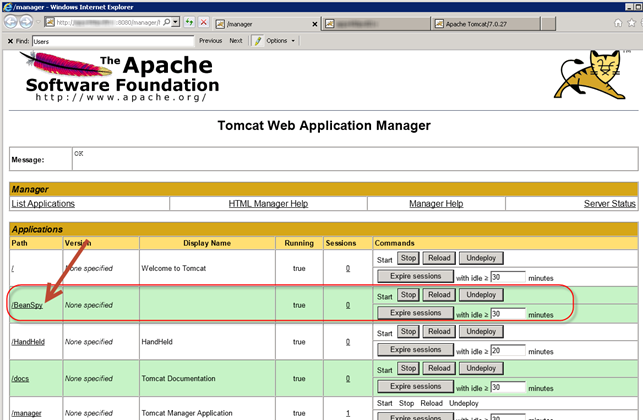
You can also view BeanSpy by accessing the web manager using this URL:
http://TOMCATSERVERNAME:8080/manager
Here are the steps to configure SCOM to monitor Tomcat running as a windows service:
Download OpsMgr_MP_Tomcat.docx and SC2012OM_JEE_MP.msi. from:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29270
Run SC2012OM_JEE_MP.msi. This will extract all JEE management packs.
Now that the management packs are extracted. Import these JEE Monitoring packs into SCOM 2012 for Tomcat:
Libraries monitoring packs:
Microsoft.JEE.Library.mpb
Microsoft.JEE.Templates.Library.mpb
Tomcat monitoring packs:
Microsoft.JEE.Tomcat.Library.mp
Microsoft.JEE.Tomcat.5.mp
Microsoft.JEE.Tomcat.6.mp
Microsoft.JEE.Tomcat.7.mp
(NOTE: Only import MP’s for your version/s of Tomcat.)
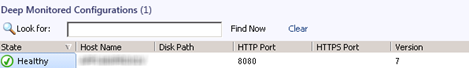
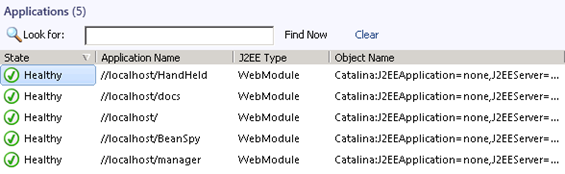
As stated in the beginning of this post Tomcat running as a windows service will not automatically be discovered.
The following two screenshots demonstrate what you will see.
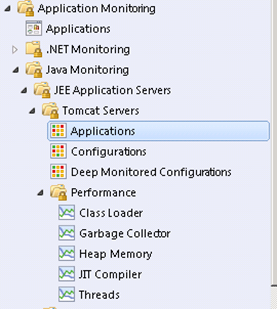
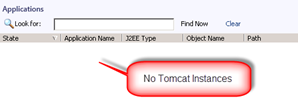
There are two options to discover the Tomcat servers when they are running as a windows service.
#1 Run your Tomcat instances as a process instead of a Windows service.
#2 Use some PowerShell scripts to discover the Tomcat instances.
In this post we are going to go with
Next you will need to use some PowerShell scripts to add the Tomcat servers. You will need these PowerShell scripts:
JEEAppServerLibrary.ps1
NewJEEAppServer.ps1
RemoveJEEAppServer.ps1
I found them in D:\Program Files\System Center 2012\Operations Manager\Server\Health Service State\Resources there
are a bunch of numbered folders and the scripts will be in separate folders.
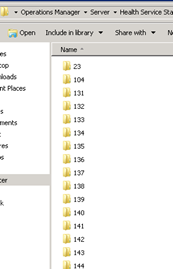
It is best to run a search to find those PowerShell scripts.
You will want to use this script to add a new Tomcat Instance: NewJEEAppServer.ps1.
Here is the help output on the NewJEEAppServer script so you can see the syntax.
Discovers JEE App Servers into Operations Manager.
BeanSpy should be deployed to each application server to be discovered.
Input:
The script accepts a number of JEE App Servers on the input pipe.
Each JEE App Server is represented as a fully qualified URL, for example,
Output:
The script displays an error message for each app server it fails to discover.
Parameters:
ManagementServer – Name of OpsMgr server to use. Use current computer if not specified
JEEAppServerType – Supported types are JBoss, Tomcat, WebSphere, and WebLogic.
Will query each application server if not specified.
JEEAppServerVersion – Supported versions are JBoss 4, 5, 6, Tomcat 5, 6, 7, WebSphere 6, 7, and WebLogic 10, 11.
Will query each application server if not specified.
UserName – User name to access the App Server URL. If provided, the script will prompt for password
Target – Additional JEE App Server to discover
(done before any JEE App Server piped into the script)
help – Prints this help
Examples:
New-JEEAppServer.ps1 -Target http://www.contoso.com:8080
type c:\MyAppServers.txt | New-JEEAppServer.ps1 -JEEAppServerType WebLogic -JEEAppServerVersion 11
type c:\MyAppServers.txt | New-JEEAppServer.ps1 -UserName mymonitor
This is the syntax I used:
.\NewJEEAppServer.ps1 -Target http://SERVERNAME:8080
-ManagementServer SCOMSERVER -JEEAppServerType Tomcat -JEEAppServerVersion 7
You should see a confirmation such as:
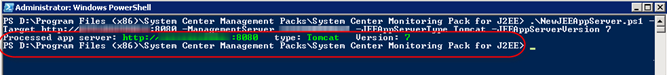
NOTE: You could place all your Tomcat instances in a text file as well.
My Tomcat instance immediately went into an error state.
![]()
My Tomcat instances require security so three things needed to be done.
#1 Create the SCOM account in Tomcat.
#2 Setup an account within Tomcat.
#3 Setup an account in SCOM and associate it with the JEE profiles
To create the SCOM account in Tomcat:
On the application server go to the Tomcat directory. Path is:
"TOMCATINSTALLPATH"\conf\
Add the user account and role to the tomcat-users.xml file.
Example:
<role rolename="monitoring"/>
<user username="scommonitor" password="secret" roles="monitoring"/>
Save the file.
To setup the JEE account in SCOM follow these steps:
Open the SCOM console and go to Administration.
Right-click Accounts, and then click Create Run As Account.
Click next on the intro page on the General Properties page:
Select Basic Authentication in the Run As Account type list.
Type a display name and a description if you want one and click next.
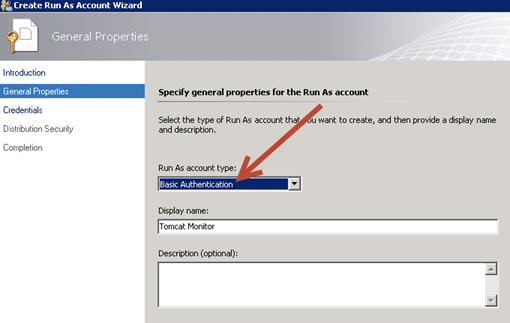
On the Credentials page, type the user name and password that you setup in Tomcat.
Now go associate this account with the JEE Invoke Account and JEE Monitoring Account profiles.
![]()
To associate the account with the JEE profiles follow these steps:
Open the SCOM console and go to Administration.
Click on Profiles.
Double-click the JEE Monitoring Account in the results pane.
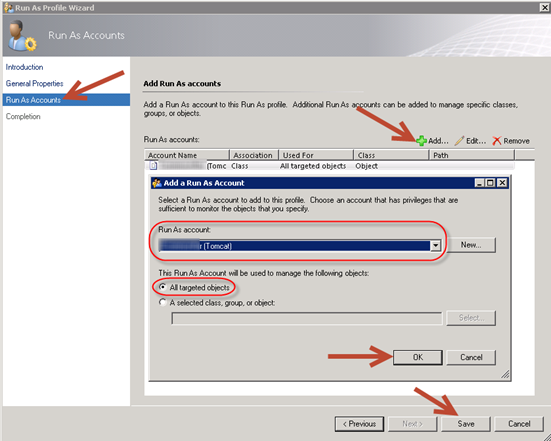
In the Run As Profile Wizard click on Run As Accounts.
Click Add and select the account you just added to SCOM.
Be sure All targeted objects is selected. Click Ok.
Click Save. Repeat for the JEE Invoke Account.
Now when you go back to the
Monitoring workspace>>Application Monitoring>>Java Monitoring>>JEE Application Servers>>Tomcat Servers
you should see your Tomcat servers go to a healthy state. This took about 5 minutes for me.